Spring MVC Part 1. MVC
영한님의 스프링 MVC 1편 - 백엔드 웹 개발 핵심 기술 강의 노트
Spring MVC Framework
MVC Pattern
Model
- View 에 출력할 데이터를 담는 역할(View 는 화면 렌더링에만 집중)
View
- Model 에 담겨있는 데이터를 사용해서 화면(HTML)을 그리는 역할
Controller
- HTTP 요청을 받아서 파라미터를 검증하고, 비즈니스 로직을 실행하는 역할
- 전달할 데이터를 조회해서 Model 을 통해 View 로 전달
스프링 MVC 전체 구조
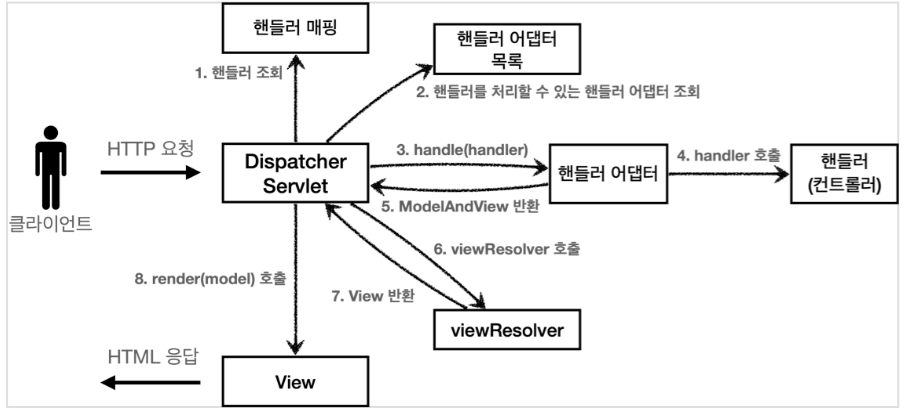
DispacherServlet
- DispatcherServlet ➜ FrameworkServlet ➜ HttpServletBean ➜ HttpServlet
- 스프링 부트는 DispacherServlet 을 서블릿으로 자동으로 등록하고, 모든 경로(urlPatterns=”/”)를 매핑
- DispacherServlet.doDispatch() 참고
핸들러 조회 : 핸들러 매핑을 통해 요청 URL에 매핑된 핸들러(컨트롤러)를 조회
핸들러 어댑터 조회 : 핸들러를 실행할 수 있는 핸들러 어댑터를 조회
핸들러 어댑터 실행 : 핸들러 어댑터를 실행
핸들러 실행 : 핸들러 어댑터가 실제 핸들러를 실행
ModelAndView 반환 : 핸들러 어댑터는 핸들러가 반환하는 정보를 ModelAndView로 변환해서 반환
viewResolver 호출 : viewResolver를 찾고 실행 (JSP의 경우 InternalResourceViewResolver 가 자동 등록&사용)
View 반환 : viewResolver는 뷰의 논리 이름을 물리 이름으로 바꾸고, 렌더링 역할을 담당하는 뷰 객체 반환 (JSP의 경우 InternalResourceView(JstlView) 를 반환하는데, 내부에 forward() 로직 존재)
뷰 렌더링 : 뷰를 통해서 뷰를 렌더링
주요 인터페이스
HandlerMapping, HandlerAdapter, ViewResolver, View
HandlerMapping & HandlerAdapter
컨트롤러 호출 과정
(1) 핸들러 매핑으로 핸들러 조회
HandlerMapping 을 순서대로 실행해서, 핸들러 찾기
- RequestMappingHandlerMapping : 애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러인 @RequestMapping에서 사용
- BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping : 스프링 빈의 이름으로 핸들러를 찾는다.
빈 이름으로 핸들러를 찾을 경우, 빈 이름으로 핸들러를 찾아주는 BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping 가 실행에 성공하고 핸들러인 Controller 를 반환
(2) 핸들러 어댑터 조회
HandlerAdapter 의 supports() 를 순서대로 호출
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter : 애노테이션 기반의 컨트롤러인 @RequestMapping에서사용
HttpRequestHandlerAdapter : HttpRequestHandler 처리
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter : Controller 인터페이스 (애노테이션X, 과거에 사용) 처리
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 가 Controller 인터페이스를 지원하므로 대상이 된다.
(3) 핸들러 어댑터 실행
디스패처 서블릿이 조회한 SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 를 실행하면서 핸들러 정보도 함께 넘겨준다.
SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter 는 핸들러인 Controller 를 내부에서 실행하고, 그 결과를 반환
ViewResolver
ViewResolver 호출 과정
(1) 핸들러 어댑터 호출
- 핸들러 어댑터를 통해 논리 뷰 이름을 획득
(2) ViewResolver 호출
논리 뷰 이름으로 viewResolver를 순서대로 호출
- BeanNameViewResolver : 빈 이름으로 뷰를 찾아서 반환
- InternalResourceViewResolver : JSP를 처리할 수 있는 뷰를 반환
논리 뷰 이름의 스프링 빈으로 등록된 뷰가 없다면 InternalResourceViewResolver 가 호출
(3)InternalResourceViewResolver
- InternalResourceView 를 반환
(4) 뷰 - InternalResourceView
- InternalResourceView 는 JSP처럼 포워드 forward() 를 호출해서 처리할 수 있는 경우에 사용
(5) view.render() view.render() 가 호출되고 InternalResourceView 는 forward() 를 사용해서 JSP를 실행
Spring MVC 기본 기능
프로젝트 설정
Jar 사용 시 항상 내장 서버(tomcat..)를 사용 (내장 서버 최적화)
War 사용 시 주로 외부 서버에 배포하는 목적으로 사용
Logging
SpringBoot 가 기본으로 제공하는 Logback 을 대부분 사용
- SLF4J interface 의 구현체인 Logback
로그 레벨 설정
application.properties 에서 log level 설정 가능
TRACE > DEBUG > INFO > WARN > ERROR
보통 개발 서버는 debug, 운영 서버는 info level
# 전체 로그 레벨 설정 (default: info) logging.level.root=info # 특정 패키지와 그 하위 로그 레벨 셀정 logging.level.hello.springmvc=trace
로그 선언
Lombok 사용 시
@Slf4jjava 코드로 선언 시
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass()); // OR private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Xxx.class)
로그 호출
// 2021-08-31 22:11:10.267 INFO 6688 --- [nio-8080-exec-6] hello.springmvc.basic.LogTestController : info log = Spring // 시간 / 로그 / 프로세스 ID / Thread Name / Class Name // Message log.trace(" trace log = {}", name); log.debug(" debug log = {}", name); log.info(" info log = {}", name); log.warn(" warn log = {}", name); log.error(" error log = {}", name);
요청 매핑
Controller Annotation
@Controller : 반환 값이 String 이면 뷰 이름으로 인식(뷰를 찾고 랜더링)
@RestController : 반환 값으로 뷰를 찾는 것이 아니라, HTTP 메시지 바디에 바로 입력
축약 Annotation
/** * 회원 목록 조회: GET /users * 회원 등록: POST /users * 회원 조회: GET /users/{userId} * 회원 수정: PATCH /users/{userId} * 회원 삭제: DELETE /users/{userId} */ @GetMapping(value = "/mapping-get-v2") public String mappingGetV2() { log.info("mapping-get-v2"); return "ok"; }@PathVariable : 최근 HTTP API는 리소스 경로에 식별자를 넣는 스타일을 선호
@GetMapping("/mapping/users/{userId}/orders/{orderId}") public String mappingPath(@PathVariable String userId, @PathVariable Long orderId) { log.info("mappingPath userId={}, orderId={}", userId, orderId); return "ok"; }특정 파라미터/헤더로 추가 매핑
- 파라미터의 경우 params, 헤더의 경우 headers
- params = {“mode=debug”,”data=good”}
/** * headers="mode", * headers="!mode" * headers="mode=debug" * headers="mode!=debug" (! = ) */ @GetMapping(value = "/mapping-header", headers = "mode=debug") public String mappingHeader() { log.info("mappingHeader"); return "ok"; }Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑 Media Type
- Server 입장에서 특정 Media Type만 받을 수 있다고 요청 헤더의 Content-Type으로 전달
/** * Content-Type 헤더 기반 추가 매핑 Media Type * consumes="application/json" * consumes="!application/json" * consumes="application/*" * consumes="*\/*" * MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE */ @PostMapping(value = "/mapping-consume", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE) public String mappingConsumes() { log.info("mappingConsumes"); return "ok"; }Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type
- Client 입장에서 특정 Media Type만 받을 수 있다고 요청 헤더의 Accept로 전달
/** * Accept 헤더 기반 Media Type * produces = "text/html" * produces = "!text/html" * produces = "text/*" * produces = "*\/*" */ @PostMapping(value = "/mapping-produce", produces = MediaType.TEXT_HTML_VALUE) public String mappingProduces() { log.info("mappingProduces"); return "ok"; }
HTTP Request
HttpServletRequest request
HttpServletResponse response
HttpMethod httpMethod
- HTTP 메서드를 조회 (org.springframework.http.HttpMethod)
Locale locale
- Locale 정보를 조회
@RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap
- 모든 HTTP 헤더를 MultiValueMap 형식으로 조회
@RequestHeader(“host”) String host
특정 HTTP 헤더를 조회
속성 (required, defaultValue)
@CookieValue(value = “myCookie”, required = false) String cookie
특정 쿠키를 조회
속성 (required, defaultValue)
Http Request Data
클라이언트에서 서버로 데이터를 전달하는 방법
GET - Query Parameter
- /url?username=hello&age=20
- URL Query Parameter에 데이터를 포함해서 전달
- ex) 검색, 필터, 페이징 등
POST - HTML Form
- content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
- Message Body에 Query Parameter 형식으로 전달 (username=hello&age=20)
- ex) 회원 가입, 상품 주문, HTML Form
HTTP message body에 데이터를 직접 담아서 요청
- HTTP API에서 주로 사용, JSON, XML, TEXT
- POST, PUT, PATCH
@RequestParam
- Get, Post 방식의 Query Parameter binding
@RequestParam(value="name" required = false, defaultValue = "-1") String name
파라미터 이름으로 바인딩
- request.getParameter(“name”) 와 동일한 효과
생략
- HTTP 파라미터 이름이 변수 이름과 같으면 value name 생략 가능
- String, int 등 단순 타입이면 @RequestParam 생략 가능
required
- 파라미터 필수 여부 (default = true )
defaultValue
- 기본 값 적용 (빈 문자도 기본 값으로 처리)
requestParamMap
- 모든 요청 파라미터 받기
- @RequestParam Map<String, Object> paramMap
- paramMap.get(“username”)
- 파라미터 값이 여러개라면 MultiValueMap 사용
@ResponseBody
- String return 시 View 조회를 무시하고, HTTP message body에 직접 해당 내용 입력
@ModelAttribute
바인딩할 객체 생성
요청 파라미터의 이름으로 바인딩 객체의 프로퍼티를 찾고, 해당 프로퍼티의 setter를 호출해서 파라미터의 값을 입력(바인딩)
- ex) 파라미터 이름이 username 이면 setUsername() 메서드를 찾아 호출하면서 값을 입력
HTTP message body
TEXT
HTTP Message Body Data 를 InputStream 을 사용해서 직접 읽을 수도 있지만, Spring MVC는 HttpEntity 지원
/** * HttpEntity: HTTP header, body 정보를 편리하게 조회 및 응답 * - HttpMessageConverter 사용 -> StringHttpMessageConverter 적용 */ @PostMapping("/request-body-string") public HttpEntity<String> requestBodyString(HttpEntity<String> httpEntity) { String messageBody = httpEntity.getBody(); log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody); return new HttpEntity<>("ok"); }HttpEntity를 상속받은 RequestEntity, ResponseEntity
- RequestEntity : HttpMethod, url 정보 등 추가 정보 제공
- ResponseEntity : HTTP 상태 코드 설정 가능
return new ResponseEntity<String>("Hello World", responseHeaders, HttpStatus.CREATED)
@RequestBody 사용
- header 가 필요하다면 @RequestHeader
@ResponseBody @PostMapping("/request-body-string") public String requestBodyString(@RequestBody String messageBody) { log.info("messageBody={}", messageBody); return "ok"; }
JSON
@RequestBody
- 생략 불가능(생략 시 @ModelAttribute 적용)
HttpMessageConverter 사용 -> MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
- content-type: application/json
응답의 경우에도 @ResponseBody 를 사용하면 해당 객체를 HTTP 메시지 바디에 직접 넣어줄 수 있음
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @ResponseBody @PostMapping("/request-body-json") public String requestBodyJson(@RequestBody HelloData data) { log.info("username={}, age={}", data.getUsername(), data.getAge()); return "ok"; }@RequestBody 요청 : JSON 요청 -> HttpMessageConverter(JSON) -> 객체
- contenttype: application/json
@ResponseBody 응답 : 객체 -> HttpMessageConverter(JSON) -> JSON 응답
- Accept: application/json
HTTP Response
Spring Response Data 생성 방법
정적 리소스
- HTML, css, js 제공
- 기본 경로 :
src/main/resources/static- Path :
src/main/resources/static/basic/hello-form.html - URI :
http://localhost:8080/basic/hello-form.html
- Path :
View Template 사용
- 동적인 HTML 제공
기본 경로 :
src/main/resources/templates- Path :
src/main/resources/templates/response/hello.html
@RequestMapping("/response-view") public String responseView(Model model) { model.addAttribute("data", "hello!!"); return "response/hello"; }- Path :
HTTP Message 사용
- HTTP API - HTTP Message Body에 데이터를 담아 제공
HTTP message body
TEXT
ResponseBody
@ResponseBody @GetMapping("/response-body-string") public String responseBody() { return "ok"; }ResponseEntity
- 응답코드를 동적으로 변경 시 사용
@GetMapping("/response-body-string") public ResponseEntity<String> responseBody() { return new ResponseEntity<>("ok", HttpStatus.OK); }
JSON
ResponseBody
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) @ResponseBody @GetMapping("/response-body-json") public HelloData responseBodyJson() { HelloData helloData = new HelloData(); helloData.setUsername("userA"); helloData.setAge(20); return helloData; }ResponseEntity
- 응답코드를 동적으로 변경 시 사용
@GetMapping("/response-body-json") public ResponseEntity<HelloData> responseBodyJson() { HelloData helloData = new HelloData(); helloData.setUsername("userA"); helloData.setAge(20); return new ResponseEntity<>(helloData, HttpStatus.OK); }
HTTP Message Converter
HTTP Message Converter 적용 시기
- HTTP 요청: @RequestBody, HttpEntity(RequestEntity)
- HTTP 응답: @ResponseBody, HttpEntity(ResponseEntity)
Spring Boot Base Message Converter
0_ ByteArrayHttpMessageConverter
- byte[] 데이터를 처리
- 클래스 타입: byte[] , content-type: */*
- 요청 ex) @RequestBody byte[] data
- 응답 ex) @ResponseBody return byte[] 쓰기 content-type application/octet-stream
1_ StringHttpMessageConverter
- String 문자로 데이터를 처리한다.
- 클래스 타입: String , content-type: */*
- 요청 ex) @RequestBody String data
- 응답 ex) @ResponseBody return “ok” 쓰기 content-type text/plain
2_ MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter
- application/json
- 클래스 타입: 객체 또는 HashMap, content-type: application/json 관련
- 요청 ex) @RequestBody HelloData data
- 응답 ex) @ResponseBody return helloData 쓰기 content-type application/json 관련
Request Mapping Handler Adapter 구조
- HTTP Message Converter 는 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter -> ArgumentResolver, Handler -> ReturnValueHandler 에서 사용되어 필요한 객체를 생성
ArgumentResolver
파라미터를 유연하게 처리
- 애노테이션 기반 컨트롤러를 처리하는 HandlerMethodArgumentResolver 는 supportsParameter() 를 호출해서 해당 파라미터를 지원하는지 체크
- 지원하면 resolveArgument() 를 호출해서 핸들러가 필요로 하는 다양한 값(객체)을 생성
- 이렇게 생성된 객체가 핸들러(컨트롤러) 호출 시 넘어 감
ReturnValueHandler
HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler 는 ArgumentResolver 와 비슷한 방식으로 응답값을 변환 및 처리
PRG (Post/Redirect/Get)
- 등록을 완료하고 웹 브라우저를 새로고침 시 중복 등록되는 오류 해결
- 상품 등록 폼 이동
- 상품 저장 및 삼품 상세 페이지로 redirect
- 상품 상세페이지 이동
스프링 완전 정복 로드맵
- 스프링 입문 > 코드로 배우는 스프링 부트, 웹 MVC, DB 접근 기술
- 스프링 핵심 원리 > 기본편
- 모든 개발자를 위한 HTTP 웹 기본 지식
- 스프링 웹 MVC 1편
- 스프링 웹 MVC 2편
- 스프링 DB 1편 > 데이터 접근 핵심 원리
- 스프링 DB 2편 > 데이터 접근 활용 기술
- 스프링 핵심 원리 > 고급편
- 실전! 스프링 부트